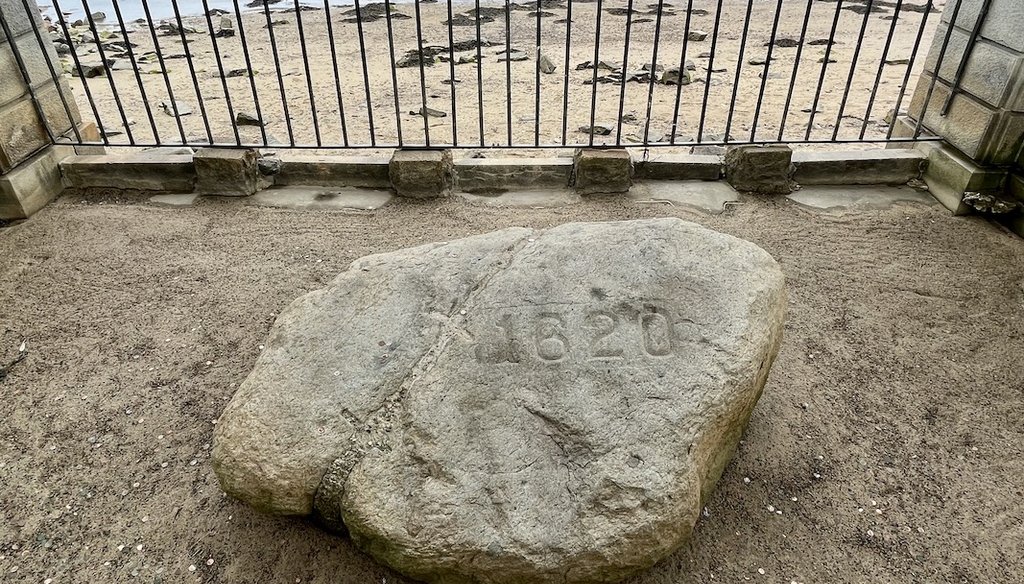Our only agenda is to publish the truth so you can be an informed participant in democracy.
We need your help.


Plymouth Rock, located at Pilgrim Memorial State Park in Plymouth, Massachusetts, on July 18, 2022. (Madison Czopek)
There is no evidence Plymouth Rock is the exact boulder where Pilgrims first disembarked the Mayflower in Plymouth in 1620, nor that it was found at sea level. The rock has also been moved several times since it was identified.
Plymouth Rock has been submerged before, during extreme weather and exceptionally high tides. Experts said it is not a useful landmark for measuring sea level changes.
Global sea levels are rising at an increasing rate.
Legend has it that, upon arriving in North America, the Pilgrims stepped off the Mayflower onto the large boulder that now sits in a place of prominence on the Plymouth, Massachusetts, waterfront.
Plymouth Rock is a well-known tourist attraction, but its connection to early U.S. history is unproven. And despite what some social media users have claimed, the landmark cannot be used to disprove that sea levels are rising.
An Instagram user shared a July 17 meme about the rock that read, "Plymouth Rock, 2022 still at sea level."
On July 12, a Facebook user shared another meme featuring two pictures of Plymouth Rock side by side, one labeled "1620 at sea level" and the other "2022 still at sea level."

(Screengrab from Facebook.)
The posts were flagged as part of Facebook’s efforts to combat false news and misinformation on its News Feed. (Read more about our partnership with Facebook.)
These Plymouth Rock memes do not prove that sea levels remain unchanged; the posts are false and misleading.
There is no evidence the rock proudly displayed under the portico in Plymouth today is the exact place where Pilgrims first disembarked the Mayflower in Plymouth, much less that it was found at sea level. (The Pilgrims first landed in Provincetown, Massachusetts, on Nov. 11, 1620. The Mayflower anchored in Plymouth Harbor a few weeks later.)
There are two primary accounts of the Pilgrims’ Plymouth landing, but "both simply say that the Pilgrims landed. Neither mentions any rocks in their account of the landing," said Plymouth’s Pilgrim Hall Museum’s website. "The first references to Plymouth Rock are found over 100 years after the actual landing."
The National Museum of American History site refers to the story of the Pilgrims landing at Plymouth Rock as "oral tradition," and said no contemporary accounts of the landing mention a rock.
Plymouth’s tourism website said in 1741 an elder identified Plymouth Rock as the exact landing spot. Although the veracity of the elder’s claim is unknown, Plymouth Rock "quickly became an American icon," the site added.
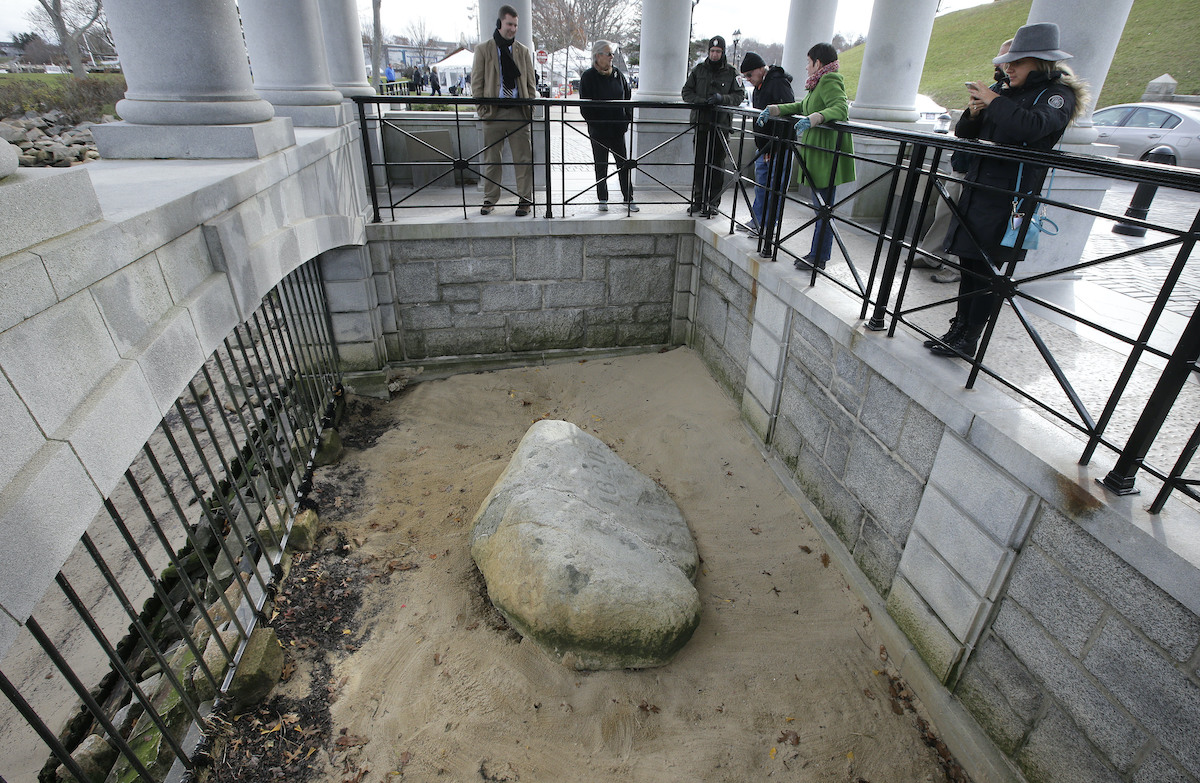

Visitors stand in a pavilion while looking at Plymouth Rock, in Plymouth, Massachusetts, on Nov. 18, 2018. (AP)
Once the boulder was identified as Plymouth Rock, its nomadic history began.
"In 1774, a team attempted to move the rock from shore and place it next to Plymouth’s liberty pole in the town square," said the National Museum of American History. "Before it could be removed from the beach, it accidentally broke in two."
One part of the rock remained in place; the other piece was moved to the town square.
More than 100 years later in 1880, "the two pieces were reunited back on the shore and cemented together," the National Museum of American History said. In most images of the rock, it is easy to see where it was fused back together. Pilgrim Hall Museum’s website said "1620" was also cut into Plymouth Rock in 1880.
In 1920, the rock was moved again, when Plymouth’s waterfront was redesigned and the shoreline was rebuilt, according to Pilgrim Hall Museum’s site.
The rock has also been underwater before, during extreme weather and exceptionally high tides called king tides.
Plymouth Rock yesterday vs today. pic.twitter.com/rW9Rko4Nkn
— MA Sharks 🦈 (@MA_Sharks) March 3, 2018
#KingTide in Plymouth, MA. Pilgrims would have got their feet wet landing on #PlymouthRock today. @ericfisher @Plymouth_400 pic.twitter.com/DxgQQXxu3J
— MA Sharks 🦈 (@MA_Sharks) November 15, 2016
Furthermore, experts said the rock is not a useful landmark for measuring sea level changes.
Michael Oppenheimer, a Princeton University professor of geosciences and international affairs, said a single, stationary object "anchored in bedrock and free of tectonic activity" can sometimes be used to measure local sea levels.
"But all it can indicate is local sea level, not ‘sea levels’ generally or the global mean rise," Oppenheimer said. Local sea level rise can significantly differ from the global mean sea level rise because of land sinking or tectonic activity, he said.
Gary Griggs, a University of California, Santa Cruz, professor of earth sciences, said the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has been tracking sea levels relative to land in Boston, near Plymouth Rock, for 100 years. These records show that sea levels have risen about 11.4 inches in the past century.
Satellite data, which has been used to measure sea level rise since 1993, indicates an average rate of global sea level rise of about 13.9 inches per century, Griggs said. That rate is accelerating; over the past decade, the rate has increased to about 19.7 inches per 100 years, he said.
"This is relatively simple science, and there are no alternate interpretations or facts," Griggs said. "Sea-level rise is directly connected to a warming climate. The warmer the planet gets, the more sea water expands, and the more ice melts, all adding to sea level."
Oppenheimer also said global mean sea levels are rising annually and that the rise is accelerating. "There is no doubt about this," he said.
Rising sea levels cause problems, some of which have already begun, Oppenheimer said.
"So-called nuisance or fair-weather flooding has increased in frequency, meaning that high tides now flood streets on a regular basis along the coast in many states — up to 10 times as frequently as 50 years ago," he said. "Furthermore, in large coastal storms, flood risk is increasing as water penetrates inland further and to higher elevation."
There’s no proof that Plymouth Rock was at sea level when it might have welcomed the Pilgrims in 1620. The rock has also moved several times in the past 400 years and is sometimes submerged during high tides and extreme weather. Experts said that Plymouth Rock is not useful for evaluating sea level changes. That sea levels are rising, however, is undisputed.
We rate this claim False.
RELATED: What does extreme weather tell us about climate change?
RELATED: Fact-checks about climate change
Email exchange with Gary Griggs, a distinguished professor of earth sciences in the earth and planetary sciences department at University of California, Santa Cruz’s Institute of Marine Sciences, July 18, 2022
Email exchange with Michael Oppenheimer, a professor of geosciences and international affairs at Princeton University and the director of Princeton’s Center for Policy Research on Energy and the Environment, July 18, 2022
Instagram post, July 17, 2022
Facebook post, July 12, 2022
Snopes, "No, that Plymouth Rock meme doesn’t disprove rise in sea level," July 8, 2022
Reuters, "Fact Check-Plymouth Rock cannot provide an accurate measure of sea level," July 7, 2022
AFP Fact Check, "Plymouth Rock photo does not invalidate sea-level rise," July 14, 2022
USA Today, "Fact check: Plymouth Rock has been moved, not an accurate gauge of sea level rise since 1620," July 18, 2022
GBH News, "Here’s where in Massachusetts the Pilgrims first landed in 1620 — and it wasn’t Plymouth," Nov. 11, 2020
National Ocean Service, "What is a King Tide?" accessed July 19, 2022
Boston.com, "Here’s what Plymouth Rock looks like during a king tide," Nov. 16, 2016
Tweet from "MA Sharks" account, Nov. 15, 2016
Tweet from "MA Sharks" account, March 2, 2018
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Tides & Currents, "Relative sea level trend, 8443970 Boston, Massachusetts," accessed July 20, 2022
The Harvard Gazette, "And now, land may be sinking," Feb. 19, 2019
Discover Magazine, "Coastal Cities are sinking as sea levels rise," May 27, 2022
History.com "The real story behind Plymouth Rock," Nov. 21, 2012
In a world of wild talk and fake news, help us stand up for the facts.